Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-11-16 Origin: Site









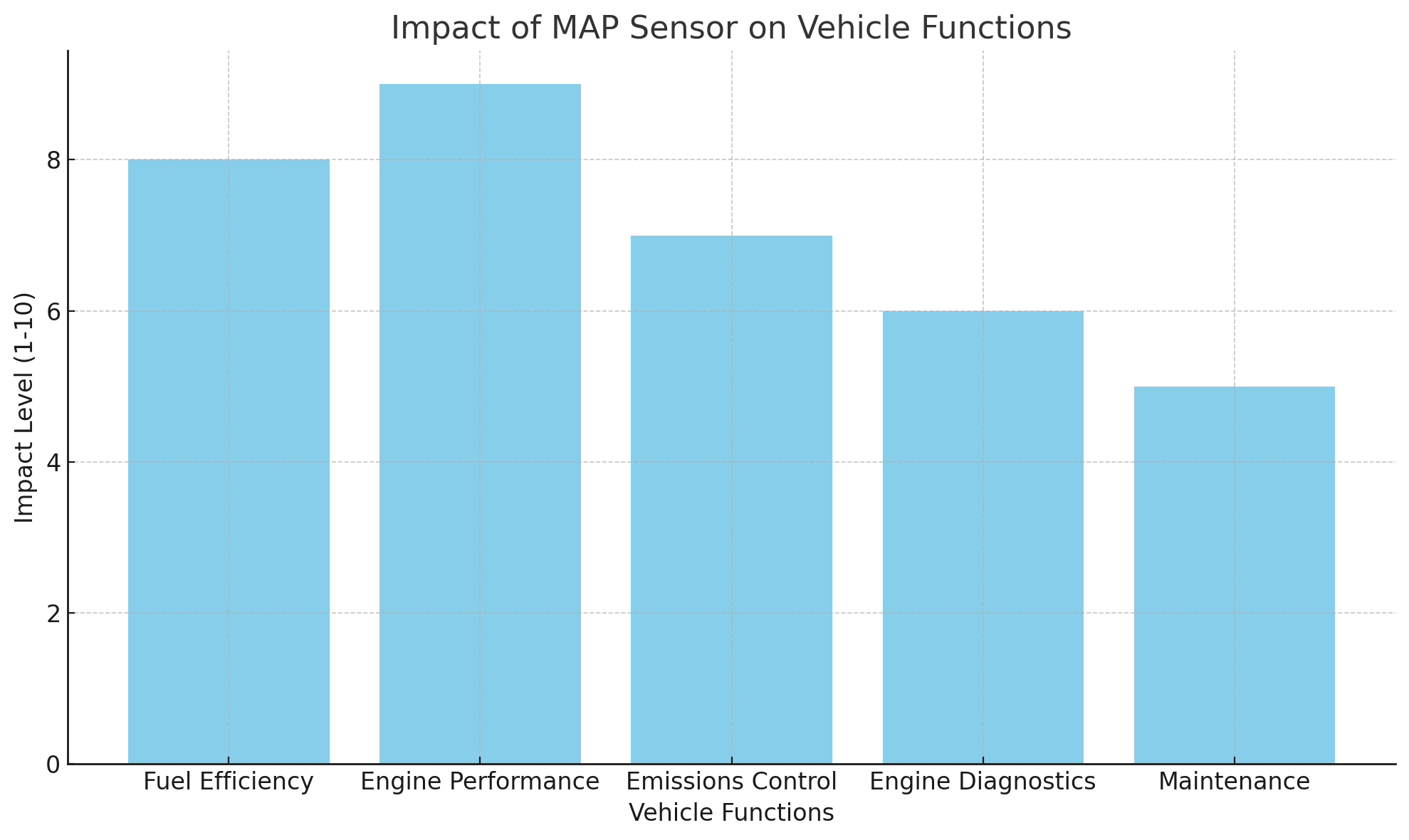
The manifold pressure sensor (MAP sensor) is essential for modern vehicle engine management. It measures the pressure inside the intake manifold, providing the engine control unit (ECU) with crucial data. This allows the ECU to optimize the fuel-air mixture, improving fuel efficiency, engine performance, and reducing emissions.
In this article, we'll explore the function of the MAP sensor, how it enhances engine performance, and why regular maintenance is vital. You will learn how to diagnose and replace a faulty MAP sensor to keep your engine running smoothly.
A manifold pressure sensor is a sensor used in internal combustion engines to monitor the pressure inside the intake manifold. The intake manifold is where the air mixes with the fuel before entering the combustion chamber. The MAP sensor measures the pressure at this location and sends real-time data to the engine control unit (ECU), which uses it to calculate the engine load and adjust fuel injection and ignition timing. By maintaining the right air-fuel ratio, the sensor ensures efficient combustion, optimal engine performance, and reduced emissions.
The MAP sensor directly influences engine performance by providing critical data that helps the ECU optimize the air-fuel mixture. When the engine accelerates, the air pressure in the intake manifold changes, and the MAP sensor detects these variations. This data allows the ECU to adjust the fuel injection rate and ignition timing to match the engine load. By making these adjustments, the MAP sensor ensures that the engine runs smoothly and efficiently, providing maximum power output while maintaining fuel economy.
The accuracy of the pressure readings provided by the MAP sensor is essential for the proper functioning of the engine. Incorrect pressure data can lead to improper fuel-air mixture adjustments, causing poor engine performance, reduced fuel efficiency, and higher emissions. The MAP sensor ensures that the ECU receives the precise data needed for optimal engine operation, which helps prevent issues such as engine knocking, misfires, and rough idling. Maintaining the accuracy of the MAP sensor's readings is crucial for engine longevity and efficiency.
The MAP sensor works by detecting changes in pressure within the intake manifold using piezoresistive materials. These materials change their electrical resistance in response to pressure variations. The sensor converts the change in resistance into an electrical signal, which is then sent to the engine control unit. The ECU uses this data to calculate engine load and adjust various engine parameters like fuel injection and ignition timing. This constant monitoring of intake pressure allows the engine to adapt to changing driving conditions, ensuring smooth and efficient performance.
Once the MAP sensor detects the changes in pressure, it converts this information into an electrical signal that the engine control unit (ECU) can process. The sensor typically sends a voltage signal that corresponds to the pressure level inside the intake manifold. This signal is amplified within the sensor to ensure accuracy and clarity before being transmitted to the ECU. The ECU processes this information and makes real-time adjustments to the engine’s fuel injection and ignition systems, optimizing performance and efficiency.
There are different types of MAP sensors, each suited for specific applications. The three main types are:
● Absolute Pressure Sensors: These measure the total pressure in the intake manifold relative to a perfect vacuum, making them ideal for monitoring manifold pressure in varying altitudes or weather conditions.
● Gauge Pressure Sensors: These measure the pressure relative to the surrounding atmospheric pressure. They are commonly used in vehicles where atmospheric conditions significantly impact engine performance.
● Differential Pressure Sensors: These measure the pressure difference between two points, such as the intake manifold and the exhaust system. These sensors are often used in more complex engine systems to detect issues such as blockages or leaks.
Understanding the differences between these types of sensors helps vehicle owners choose the appropriate MAP sensor for their engine’s needs.
One of the primary roles of the MAP sensor is to help maintain the ideal air-fuel mixture. Accurate pressure readings allow the ECU to adjust the amount of fuel injected into the engine, ensuring that combustion is efficient. This optimization not only improves engine performance but also reduces harmful emissions. By ensuring that the air-fuel ratio is perfect for all driving conditions, the MAP sensor helps minimize the release of unburned fuel and other pollutants into the atmosphere.
The MAP sensor is also essential for diagnosing potential engine issues. It helps the ECU detect problems like vacuum leaks, faulty components, or poor engine performance. For instance, if the MAP sensor detects abnormal pressure levels, it can trigger a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that can be read by a mechanic using a scan tool. These codes provide valuable insights into the cause of the problem, allowing for quicker and more accurate repairs.
By providing continuous, real-time data on the intake manifold pressure, the MAP sensor enables the engine to operate more efficiently. The sensor’s data allows the ECU to make precise adjustments to fuel injection and ignition timing, which helps reduce fuel consumption and improve power output. This contributes to a more economical engine, allowing drivers to enjoy better fuel efficiency and reduced operating costs.
Engine Activity |
MAP Sensor Role |
Impact on Performance |
Acceleration |
Adjusts air-fuel mixture for more fuel injection |
Smoother and faster acceleration |
Idle |
Maintains steady pressure for consistent air-fuel ratio |
Prevents rough idling |
Cruising |
Monitors intake pressure to maintain fuel efficiency |
Ensures optimal fuel consumption |
A faulty MAP sensor can significantly affect vehicle performance. Common symptoms of a malfunctioning MAP sensor include:
● Poor acceleration: A bad MAP sensor can lead to a sluggish response when accelerating due to incorrect fuel-air mixture adjustments.
● Rough idling: The engine may idle roughly or stall if the MAP sensor provides incorrect pressure data to the ECU.
● Reduced fuel efficiency: A malfunctioning sensor can cause the engine to consume more fuel than necessary by sending incorrect pressure readings to the ECU.
When the MAP sensor fails to provide accurate pressure data, it disrupts the engine's air-fuel ratio, leading to poor performance. The ECU struggles to adjust fuel injection and ignition timing, which can result in misfires, engine knocking, and reduced engine power. These issues not only affect the driving experience but can also lead to more serious engine problems if left unresolved.
If the MAP sensor detects abnormal readings, the engine control unit (ECU) may trigger the check engine light. The system may also store diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), which can be read with an OBD-II scanner. Common error codes related to a faulty MAP sensor include P0105 (MAP Circuit Failure) and P0106 (MAP/Barometric Pressure Circuit Range/Performance Issue). These codes help mechanics pinpoint the issue quickly and efficiently.
Symptom |
Description |
Impact on Engine Performance |
Poor Acceleration |
Delay or hesitation when accelerating |
Decreased engine responsiveness |
Rough Idling |
Engine shakes or stutters at idle speed |
Affects smooth engine operation |
Reduced Fuel Efficiency |
Noticeable drop in miles per gallon (MPG) |
Increased fuel consumption |
Check Engine Light (CEL) |
Warning light illuminated on the dashboard |
Alerts user to sensor-related issues |
Diagnosing a faulty MAP sensor requires using an OBD-II scanner to check for stored error codes. Additionally, a multimeter can be used to measure the voltage output from the sensor. The sensor should show a voltage between 0.5 and 4.5 volts. A reading outside this range indicates a malfunction. Using a hand pump to test the sensor's response to changes in pressure can also help confirm whether the sensor is working correctly.
Step |
Action |
Tools Required |
Step 1: Check Voltage Output |
Use a multimeter to test the MAP sensor voltage |
Multimeter |
Step 2: Inspect Wiring |
Check for damaged or loose connections |
Visual inspection, wiring diagram |
Step 3: Test with Vacuum |
Use a hand pump to test the sensor’s response to pressure changes |
Hand pump, multimeter |
Step 4: Replace if Necessary |
Replace the MAP sensor if readings are inaccurate or damaged |
New MAP sensor, screwdriver |
If a faulty MAP sensor is diagnosed, it should be replaced promptly. The sensor is usually located near the throttle body or intake manifold. To replace it, remove any screws or bolts securing the sensor, disconnect the electrical connector, and replace the sensor with a new one. Ensure the new sensor is compatible with the vehicle model. After installation, clear any error codes from the ECU and test the vehicle to ensure proper function.
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the MAP sensor’s longevity and optimal performance. This includes periodic cleaning to remove dirt and debris, as well as inspecting vacuum lines for leaks. Keeping the sensor and its surrounding components in good condition can prevent costly repairs and improve engine performance.
Maintenance Task |
Frequency |
Importance |
Inspect for Vacuum Leaks |
Every 6 months |
Ensures accurate pressure readings |
Clean the Sensor |
Annually or as needed |
Prevents contamination affecting sensor performance |
Check Wiring and Connectors |
During routine checks |
Avoids electrical signal issues |
Replace Faulty Components |
As needed |
Restores accurate data for the ECU |

The manifold pressure sensor (MAP sensor) is essential for efficient engine performance. It helps optimize fuel efficiency and reduce emissions by monitoring the intake manifold’s pressure. Regular maintenance and timely diagnostics can prevent costly engine malfunctions. For professional MAP sensor solutions and maintenance, Langch provides high-quality products and services that ensure your vehicle operates at its best.
A: The manifold pressure sensor (MAP sensor) monitors the pressure inside the intake manifold and provides data to the engine control unit (ECU) to optimize engine performance and fuel efficiency.
A: The MAP sensor helps adjust the air-fuel mixture based on intake pressure, ensuring optimal combustion and improving fuel efficiency.
A: Common signs of a faulty MAP sensor include poor acceleration, rough idling, and decreased fuel efficiency, which can impact overall engine performance.
A: A bad MAP sensor can be diagnosed by using a multimeter to check its voltage or by checking for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) via an OBD-II scanner.
A: Yes, replacing a MAP sensor is generally straightforward, but it's important to follow proper steps to ensure it's installed correctly for optimal engine performance.
A: Regular maintenance, such as cleaning and inspecting the sensor, helps prevent sensor malfunctions and ensures the vehicle runs efficiently, saving on repair costs.
A: By optimizing the air-fuel mixture, the MAP sensor helps reduce harmful emissions, contributing to cleaner engine combustion and better environmental compliance.