Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-11-15 Origin: Site









Did you know that under-inflated tires can lead to accidents and reduced fuel efficiency? Tire pressure sensors play a crucial role in keeping your tires properly inflated.
In this article, we’ll explore where the tire pressure sensor is located, how it functions, and why it’s essential for vehicle safety. You’ll also learn how to troubleshoot and maintain your TPMS for optimal performance.
A tire pressure sensor, also known as a TPMS sensor, monitors the air pressure inside your vehicle's tires. The sensor communicates with the vehicle’s onboard system, alerting the driver when the tire pressure falls below the recommended level. This system plays a crucial role in enhancing road safety by preventing tire blowouts and improving vehicle efficiency.
The main function of the tire pressure sensor is to detect the air pressure in each tire. If the tire pressure falls below a certain threshold, the sensor sends a signal to the vehicle's computer, triggering a warning light on the dashboard. This allows the driver to take action before the tire pressure becomes critical, ensuring safe driving and optimal tire performance.
There are two primary types of TPMS: direct and indirect.
● Direct TPMS uses sensors mounted inside each tire to measure air pressure and send real-time data to the vehicle’s computer system. These sensors are highly accurate and provide precise pressure readings for each tire.
● Indirect TPMS, on the other hand, doesn’t use physical sensors inside the tire. Instead, it uses the vehicle’s ABS sensors to estimate tire pressure based on the rotation speed of each tire. This system is less accurate but more cost-effective.
Type | Location | Measurement Method | Common Vehicles |
Direct TPMS | Inside the tire, attached to valve stem | Direct measurement of tire pressure | Most modern vehicles (Nissan, Toyota, Honda, etc.) |
Indirect TPMS | Uses wheel speed sensors on the ABS system | Estimates tire pressure based on rotational speed | Some older or budget vehicles |
Direct TPMS sensors are the most commonly used. They are typically mounted inside each tire, usually attached to the valve stem. This location allows the sensor to directly measure the air pressure in the tire and send this data to the vehicle’s onboard computer.
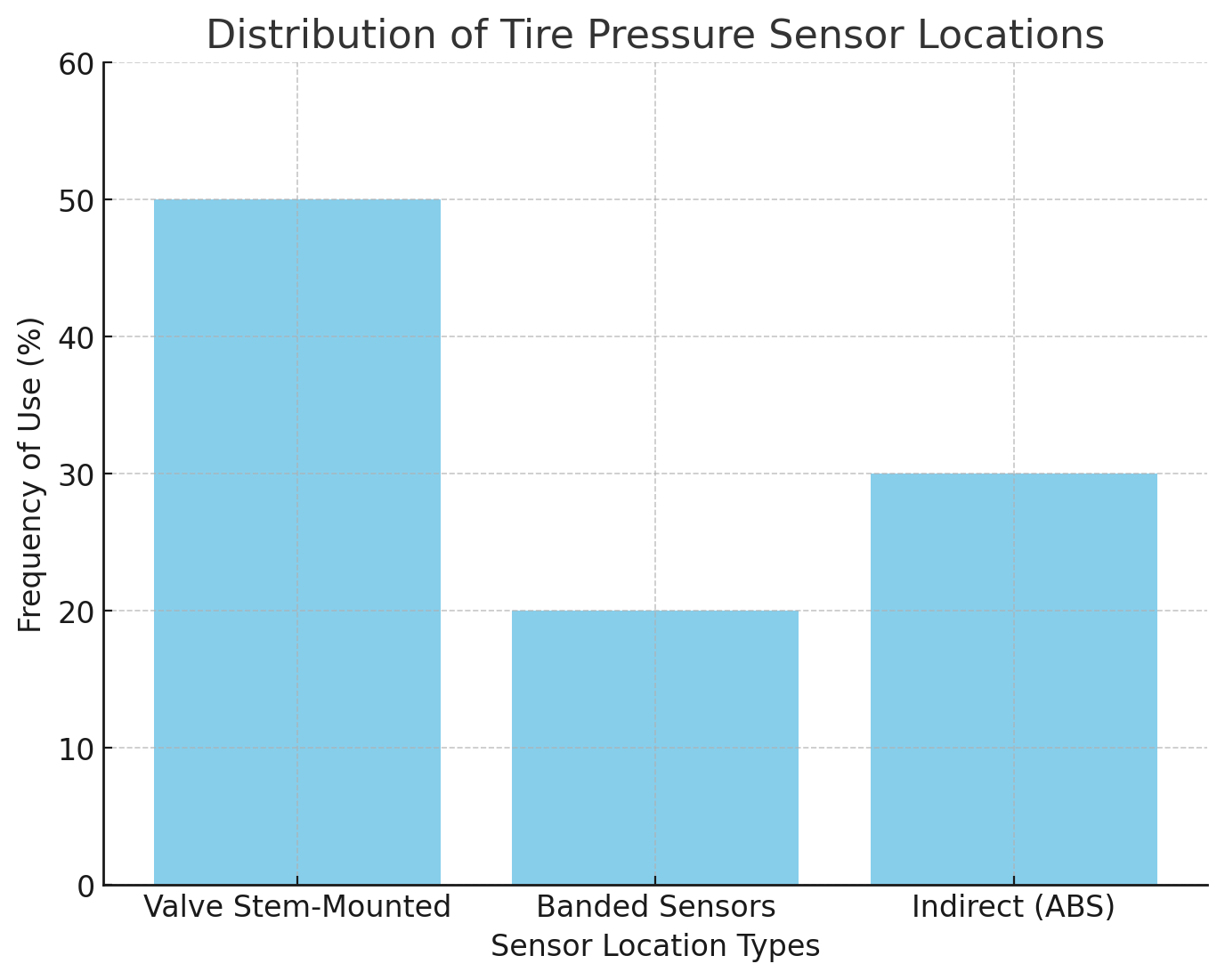
● Valve Stem-Mounted Sensors: This is the most common location for direct TPMS sensors. These sensors are integrated into the valve stem, inside the tire, where they can detect tire pressure accurately. To access the sensor, the tire must be removed from the rim.
Sensor Type | Location | Description |
Valve Stem-Mounted Sensor | Inside the tire, attached to the valve stem | The most common type of sensor, found in most vehicles |
Banded TPMS Sensor | Secured to the inner circumference of the wheel | Less common; found in some older Ford and Lincoln models |
ABS-based Sensor | Located on the wheel hub assembly (for indirect TPMS) | Uses wheel speed data to estimate pressure |
In some vehicles, especially older models, banded TPMS sensors are used. These sensors are attached to the inside of the wheel using a metal or plastic band. While less common today, these sensors are still found in many older Ford and Lincoln models. To access a banded sensor, you must remove the tire and examine the band around the inner circumference of the wheel.
Indirect TPMS does not use a physical sensor inside the tire. Instead, it uses the vehicle’s ABS sensors to monitor the wheel speed. These sensors are located near the brake rotors and detect changes in the rotational speed of the tires. If a tire’s pressure is low, it will rotate faster than the others, and the system will trigger a warning.
Direct TPMS sensors use pressure transducers and small radio transmitters. The pressure transducer measures the air pressure inside the tire, and the transmitter sends this data to the vehicle’s computer. The system is designed to alert the driver when the pressure drops below a set threshold, often around 25% below the recommended level. These sensors are powered by small batteries, which typically last 5 to 10 years, depending on usage.
Indirect TPMS does not rely on physical sensors inside the tire. Instead, it uses data from the vehicle’s ABS system to calculate tire pressure based on the rotational speed of the tires. If a tire is under-inflated, it will rotate faster than the properly inflated tires, triggering a warning light on the dashboard.
Most direct TPMS sensors are powered by small lithium batteries. These batteries are sealed within the sensor, making them non-replaceable. The lifespan of the battery typically ranges from 5 to 10 years. When the battery runs out, the sensor will no longer transmit data, requiring a replacement of the sensor unit. Indirect TPMS systems do not require a battery since they use the vehicle’s ABS sensors.
To locate the tire pressure sensor, the tire must be removed from the rim. For vehicles with direct TPMS, the sensor is usually attached to the valve stem. Once the tire is removed, you will be able to see the sensor inside the wheel. For banded sensors, look for the metal or plastic band around the wheel's inner circumference.
Tire pressure sensors come in various designs, including valve stem-mounted sensors and banded sensors. The most common design is the valve stem-mounted sensor, which is integrated into the valve stem inside the tire. These sensors are easy to access once the tire is removed. Banded sensors, though less common today, are secured around the wheel using a band and require removing the tire to access the sensor.
The location of the tire pressure sensor can vary depending on the make and model of the vehicle. For instance, while many vehicles use valve stem-mounted sensors, older models, or certain brands like Ford and Lincoln, may use banded sensors. Always refer to your vehicle’s manual for specific instructions on locating the sensor.
● Battery Failure: One of the most common issues with direct TPMS sensors is battery failure. The sensor uses a small lithium battery, which can deplete after 5 to 10 years.
● Physical Damage: The sensor may be damaged during tire changes or due to external factors like potholes or curb impacts.
● Communication Errors: Sometimes, the sensor may fail to communicate with the vehicle’s computer due to issues like signal interference or a faulty sensor.
Issue | Cause | Solution |
Faulty Sensor | Damaged sensor or worn-out battery | Replace the sensor |
Low Battery | Sensor battery depletion | Replace the sensor battery or the entire sensor |
Communication Error | Signal loss between sensor and vehicle computer | Check for interference or sensor damage |
If you notice a malfunctioning sensor, the first step is to check the tire pressure manually using a gauge. If the pressure is fine, but the TPMS light remains on, you may need to reset or recalibrate the system. Consult your vehicle’s manual for instructions on how to reset the TPMS. If the issue persists, the sensor may need to be replaced.
To replace a faulty TPMS sensor, you’ll need to remove the tire from the rim and access the sensor. If the sensor is valve stem-mounted, simply unbolt the sensor from the valve and replace it with a new one. After replacing the sensor, the new sensor may need to be programmed to communicate with the vehicle’s onboard system.
Step | Action | Tool Required |
Step 1 | Remove the tire from the rim | Tire changing machine, jack |
Step 2 | Deflate the tire and access the sensor | Valve core removal tool |
Step 3 | Remove the old sensor | Socket wrench |
Step 4 | Install the new sensor | Torque wrench |
Step 5 | Reinstall the tire and inflate it | Tire inflator |

Tire pressure sensors are essential for vehicle safety, helping monitor tire pressure and alerting drivers to issues. Knowing where these sensors are located allows for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. Whether your vehicle has direct or indirect TPMS, identifying the sensor’s location ensures timely issue resolution. Regular checks and replacements improve vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, and safety. If unsure about maintenance, consult a professional mechanic to ensure your TPMS is working properly. Langch offers reliable products and services to help maintain your vehicle’s safety and performance, ensuring optimal tire pressure monitoring.
A: The tire pressure sensor is typically located inside the tire, attached to the valve stem or mounted around the wheel's inner circumference.
A: The pressure sensor monitors tire pressure and sends data to the vehicle's computer to alert the driver if the pressure is low.
A: The sensor is usually mounted on the valve stem or secured with a band around the wheel, requiring tire removal for visibility.
A: Direct TPMS sensors measure tire pressure inside the tire, while indirect systems use ABS sensors to estimate pressure based on wheel speed.
A: The light could be on due to under-inflated tires, sensor malfunction, or battery failure in the sensor.
A: Replacing a faulty sensor typically requires removing the tire and valve stem. It’s advisable to consult a professional mechanic for accurate replacement and calibration.
A: Tire pressure sensors generally last 5–10 years, but they should be replaced when the battery fails or if the sensor becomes damaged.